Memory formation techniques are at the forefront of neuroscience, offering innovative approaches to understanding how memories are created and sustained in the brain. Researchers are exploring methods such as neural mapping techniques and synaptic plasticity to uncover the intricate network of neuronal signaling that contributes to our cognitive functions. A groundbreaking tool known as the EPSILON technique allows scientists to visualize these processes with unprecedented clarity, paving the way for new insights in dementia research and other memory-related disorders. By studying the synaptic connections that underpin learning, we can gain valuable knowledge about the molecular basis of memory and potentially discover therapeutic interventions. As we delve deeper into these memory formation techniques, the possibilities for improving cognitive health become ever more promising.
Exploring the intricacies of how our brain retains information brings us to an array of techniques for enhancing memory. Terms like synaptic enhancement strategies and memory retention methods align closely with ongoing studies in cognitive neuroscience. With advances in imaging technology and molecular biology, scientists can examine the synaptic changes that occur during the learning process. The EPSILON methodology, for example, represents a significant leap forward in our ability to track the dynamics of synaptic connections crucial to memory. By adopting a holistic view of memory mechanisms, we can better understand challenges like Alzheimer’s, ultimately improving therapeutic prospects.
Understanding Memory Formation Techniques
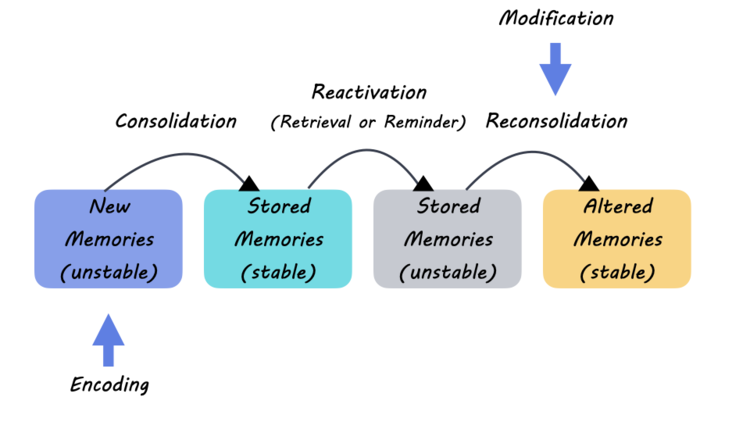
Memory formation involves complex processes that allow individuals to encode, store, and retrieve information. At its core, the brain employs **neural mapping techniques** to uncover how memories are intricately woven into the brain’s neuroanatomy. Various memory formation techniques have emerged, with researchers focusing on synaptic plasticity—the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time based on activity levels. This dynamic nature ensures that the brain adapts continually, enabling enhanced learning capabilities.
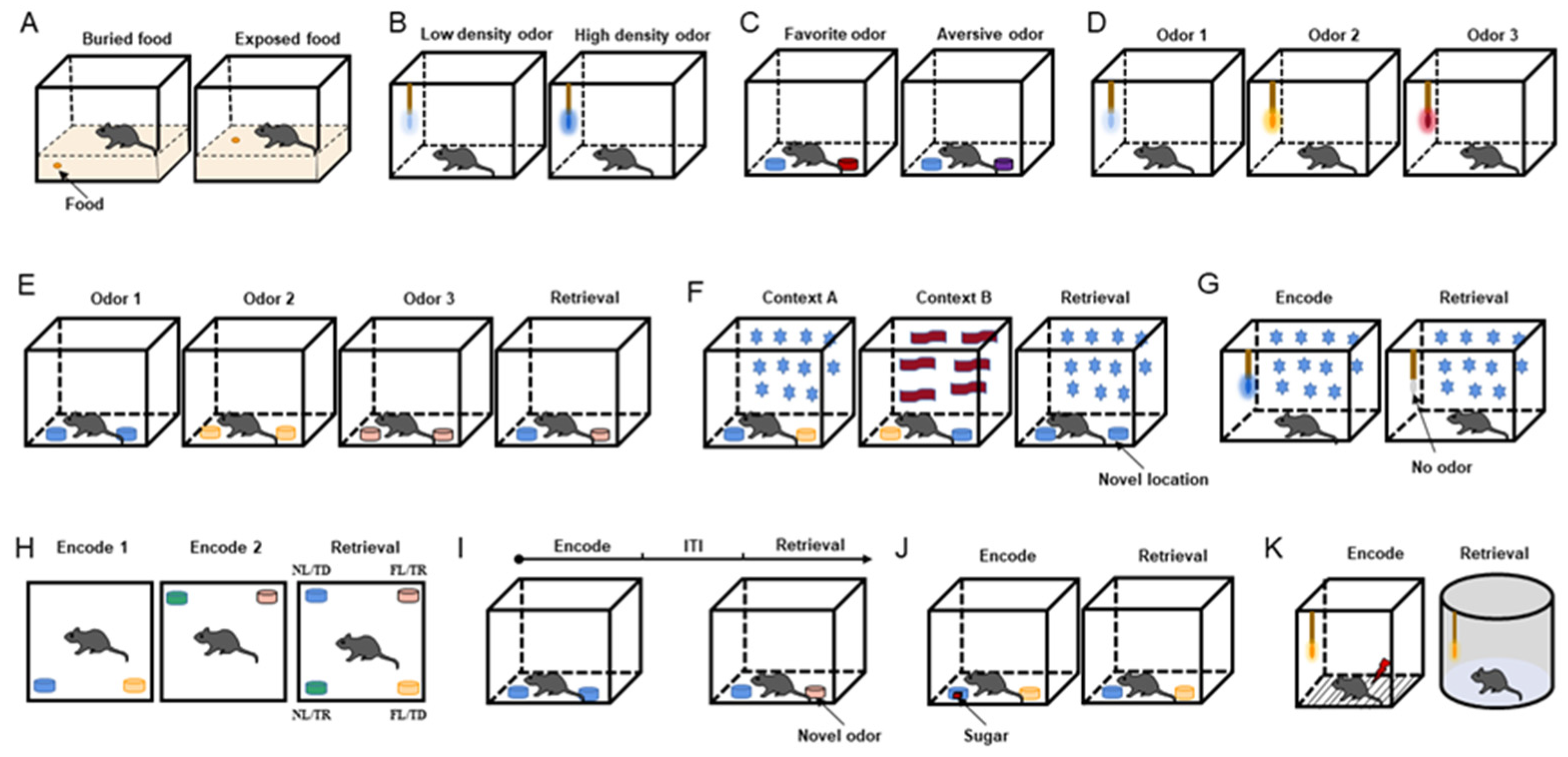
One particularly groundbreaking approach in memory formation is the use of techniques like the EPSILON method. This innovative method enhances our understanding of synaptic connections by mapping essential proteins involved in memory storage and retrieval. By employing fluorescent labeling in combination with advanced microscopy, scientists can observe the real-time behavior of **neuronal signaling**, revealing how specific synaptic interactions contribute to memory formation across different contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some effective memory formation techniques related to synaptic plasticity?
Memory formation techniques centered around synaptic plasticity involve understanding how synapses, or connections between neurons, strengthen or weaken. Techniques such as repetitive practice, spaced learning, and engaging multiple senses can enhance synaptic plasticity, thereby improving memory retention. The recent research utilizing the EPSILON technique shows how mapping synaptic behavior can further optimize these memory formation strategies.
How does the EPSILON technique contribute to our understanding of memory formation?
The EPSILON technique, or Extracellular Protein Surface Labeling in Neurons, offers groundbreaking insights into memory formation by enabling researchers to visualize the behavior of key proteins like AMPARs (alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors) involved in synaptic plasticity. This detailed mapping helps to elucidate how memories are stored and how synaptic changes influence learning, making it a pivotal tool in dementia research.
What role does neuronal signaling play in memory formation techniques?
Neuronal signaling is crucial in memory formation techniques as it refers to the process by which neurons communicate and transmit information. Understanding this signaling helps in techniques aimed at enhancing memory, as it illustrates how synaptic connections are formed and modified. Techniques focusing on improving neuronal signaling can lead to better learning outcomes and effective strategies in conditions like dementia.
Can memory formation techniques help in dementia research?
Yes, memory formation techniques, especially those informed by discoveries like the EPSILON method, greatly assist dementia research. By providing insights into synaptic plasticity and neuronal signaling, these techniques pave the way for developing therapies that target memory deficits associated with dementia. Researchers can apply findings from such techniques to understand the underlying mechanisms of memory loss in patients.
What is the significance of synaptic plasticity in learning and memory formation techniques?
Synaptic plasticity is fundamental to learning and memory formation techniques as it involves the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, directly affecting memory retention. Techniques that leverage this concept, like spaced repetition and active recall, can optimize synaptic plasticity, enhancing the learning process and leading to better memory formation overall.
How might groundbreaking techniques in memory formation impact future therapies for memory impairments?
Groundbreaking techniques, such as those utilized in recent studies mapping synaptic behavior, provide critical insights into the molecular mechanisms of memory. Such advancements can lead to innovative therapies aimed at enhancing synaptic plasticity and neuronal signaling, ultimately creating more effective treatments for memory impairments, including those seen in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| New Technique | Extracellular Protein Surface Labeling in Neurons (EPSILON) maps molecular mechanisms of memory formation. |
| Synaptic Plasticity | The technique shows how connections between neurons strengthen or weaken during memory consolidation. |
| Research Applications | Potential to develop new therapies for diseases like dementia and Alzheimer’s by understanding synaptic behavior. |
| Future Directions | EPSILON may lead to insights into cognitive functions and memory impairments, with tools being shared globally. |
Summary
Memory formation techniques play a crucial role in understanding how the brain encodes experiences and knowledge. Recent advancements, such as the EPSILON technique developed by Harvard researchers, offer unprecedented insights into the synaptic changes associated with memory. This cutting-edge method not only enhances our comprehension of synaptic plasticity but also paves the way for innovative therapeutic strategies aimed at addressing memory-related disorders like dementia. By enabling detailed observation of molecular processes, these techniques hold the promise of unlocking new frontiers in neural research, leading to better treatment options for those affected by cognitive impairments.