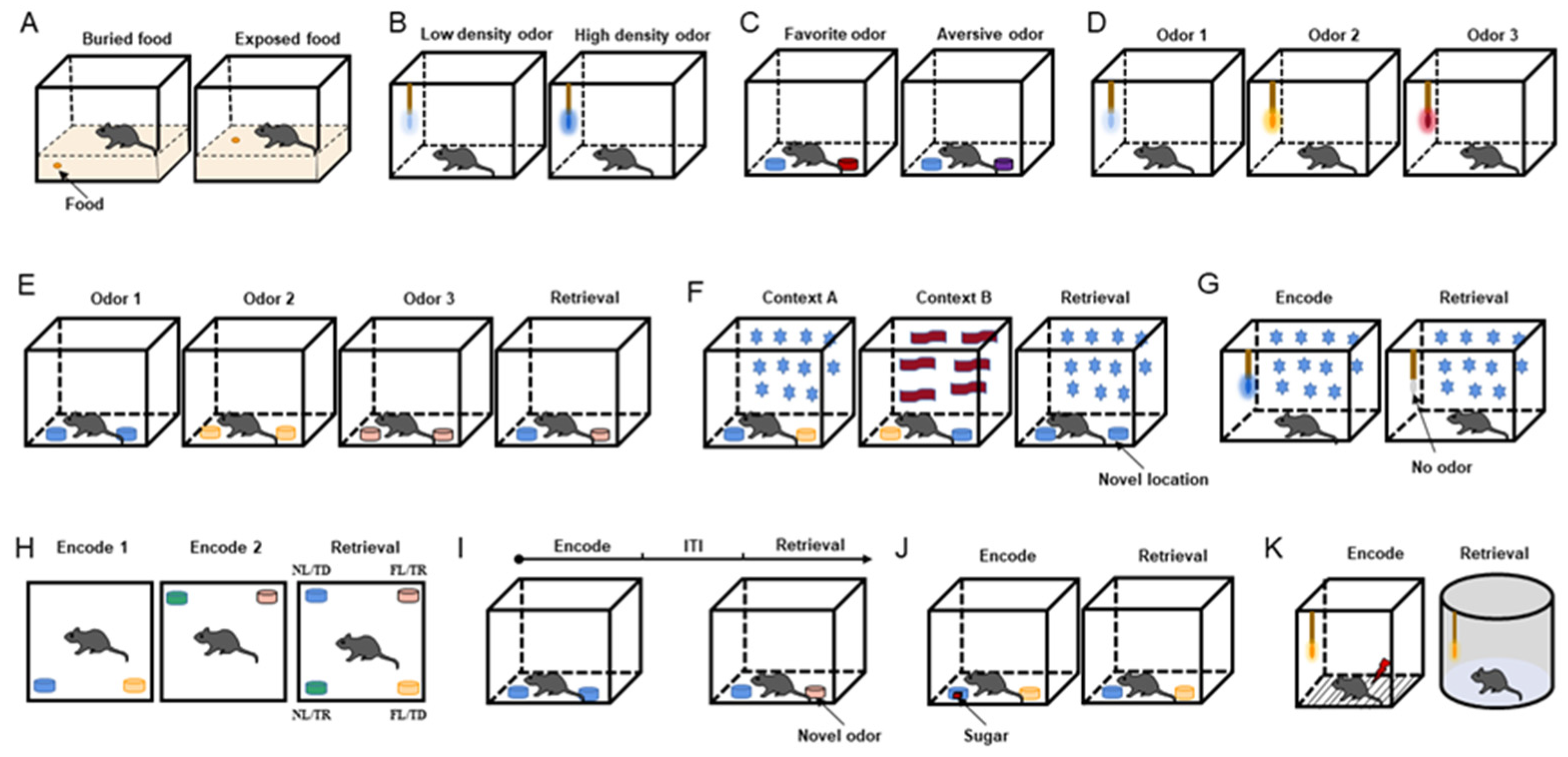
The recent development of olfactory tests for Alzheimer’s offers promising insights into early detection methods for this debilitating neurodegenerative disease. Researchers from Mass General Brigham have pioneered a straightforward smell test to assess individuals’ olfactory capabilities, revealing a potential link between poor smell discrimination and Alzheimer’s risk. This innovative cognitive impairment test allows participants to identify scents at home, making it a convenient tool for monitoring changes in sensory perception. With Alzheimer’s risk assessment becoming increasingly critical, these findings underscore how subtle shifts in smell can be an early warning sign of cognitive decline. By incorporating this olfactory test into routine screenings, we might enhance early detection of Alzheimer’s, paving the way for timely interventions that could slow disease progression.
A groundbreaking approach in detecting Alzheimer’s involves utilizing scent-based evaluations to determine cognitive health. This home-based smell assessment, linked with identifying cognitive decline, could offer vital insights into the onset of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s. By analyzing how well individuals recognize and remember odors, researchers can gauge potential risks well before symptoms manifest. This smell test serves as a vital component in monitoring neurological health, acting as an accessible cognitive function indicator. Incorporating such innovative assessment methods could revolutionize how we approach Alzheimer’s risk evaluation and early intervention.
The Role of Olfactory Testing in Early Detection of Alzheimer’s
Olfactory testing has emerged as a promising avenue for the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease, where researchers highlight that our sense of smell can act as an indicator of cognitive health. The recent study by the team at Mass General Brigham reveals that individuals with mild cognitive impairment often display diminished ability to identify and remember odors, correlating with an increased risk for neurodegenerative diseases. This olfactory test is significant as it offers a non-invasive and cost-effective method to assess cognitive function right from the comfort of one’s home.
By utilizing simple odor labels placed on a testing card, participants engage in a task that measures their olfactory memory and discrimination abilities. This method stands out due to its accessibility and ease of use compared to traditional cognitive assessments, making it an ideal tool for early Alzheimer’s risk assessment. Not only does this approach serve as an engaging platform for testing, but it could potentially lead to identifying those who should be monitored more closely for cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s symptoms.
Understanding Cognitive Impairment Tests: A New Frontier
Cognitive impairment tests play a pivotal role in diagnosing and understanding the progression of Alzheimer’s. The olfactory test specifically measures how well individuals can differentiate and recall specific smells, which has been shown to decline in those at risk for cognitive decline. This innovative approach aligns with emerging research that emphasizes the connection between sensory changes and neurodegenerative diseases, positioning olfactory testing as a crucial element in the broader context of cognitive health.
Additionally, integrating olfactory tests into clinical research and routine assessments could enhance the comprehension of neurodegenerative disease warning signs. As our sense of smell often diminishes gradually, monitoring this decline through simple, engaging tests could provide early insights into an individual’s cognitive trajectory, paving the way for timely intervention and management of conditions like Alzheimer’s.
The Impact of Smell on Neurodegenerative Disease Diagnosis
Recent studies underscore the increasing evidence that smell plays a critical role in diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. The aroma detection test developed at Mass General Brigham provides a unique lens through which clinicians can assess risk factors associated with these debilitating conditions. This shift towards olfactory testing highlights an important aspect of early detection in Alzheimer’s; while outward cognitive symptoms may take years to manifest, subtle changes in olfactory function can provide crucial warning signs.
Moreover, the ability to conduct this smell test at home opens new paradigms for patient engagement and self-monitoring. Older adults who may face mobility or transportation challenges can partake in this test, alleviating barriers to early diagnosis and enabling proactive health measures. By integrating simple yet effective tools like this olfactory test into the realm of Alzheimer’s risk assessment, healthcare providers can better equip patients and families to navigate the complexities surrounding cognitive health.
Advancements in Non-invasive Cognitive Health Assessments
The landscape of cognitive health assessments is evolving with advances in non-invasive testing methods. The olfactory assessment developed by the research team at Mass General Brigham exemplifies this shift. By relying on an individual’s sense of smell, researchers can create a low-stress environment that encourages participation and gives valuable insights into cognitive function. This is particularly important for older adults who may feel apprehensive about more traditional, invasive testing methods.
As studies demonstrate the efficacy of olfactory tests, they are likely to gain traction as a first-line tool in cognitive impairment screenings. The potential for these tests to be used in various languages and settings addresses a critical need for inclusivity in healthcare, ensuring that diverse populations have access to meaningful cognitive health evaluations. Such advancements could indeed revolutionize how we approach Alzheimer’s detection and inform more effective interventions.
Global Implications of Olfactory Tests in Alzheimer’s Risk Assessment
The global implications of integrating olfactory tests into Alzheimer’s risk assessment frameworks are significant, as they promise to enhance early detection across diverse populations. The ability to accurately assess cognitive decline through smell not only serves a clinical purpose but also raises awareness about the importance of olfactory function as a public health concern. Countries with limited resources for extensive cognitive testing may find olfactory assessments to be a more viable option, thereby increasing the potential for early identification of at-risk individuals.
Furthermore, as more research validates the reliability of olfactory testing, it could become a standard component of regular health check-ups for older adults. This proactive approach can lead to preventive measures that help manage cognitive decline before more serious symptoms arise. By championing olfactory tests as a key tool for Alzheimer’s risk assessment, we could foster a more informed public that empowers individuals to take charge of their cognitive health.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Diagnosis and Treatment
The future of Alzheimer’s diagnosis and treatment is promising, especially with novel methods like olfactory tests emerging on the scene. By combining sensory assessments with neuropsychological testing, researchers aim to establish a comprehensive approach to evaluating cognitive health. This multifaceted strategy could lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses, which are crucial in the management of Alzheimer’s disease and related conditions.
As we move forward, the integration of olfactory assessment tools into clinical practices will likely enhance our ability to predict not just the presence of Alzheimer’s, but also its progression over time. This shift could revolutionize treatment plans, allowing healthcare providers to tailor interventions to individual patients based on their unique cognitive profiles, ultimately improving outcomes and quality of life for those affected by this challenging neurodegenerative disease.
Societal Benefits of Early Detection of Alzheimer’s
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease brings significant societal benefits that extend beyond individual health outcomes. By identifying at-risk individuals through tools like olfactory testing, we can not only enhance early therapeutic strategies but also allocate resources more effectively. With accurate predictions of cognitive decline, families can prepare, and healthcare systems can develop tailored support mechanisms, reducing the overall burden on caregivers and the wider community.
Moreover, increasing public awareness about the signs of neurodegenerative diseases fosters a culture of proactive health. Society stands to gain immensely through initiatives promoting early detection, as they can lead to reduced healthcare costs over time and improve the overall quality of life for individuals affected by memory disorders. As more people embrace the importance of cognitive health, the integration of olfactory testing into routine medical assessments might change how we collectively approach Alzheimer’s.
The Science Behind Olfactory Dysfunction and Alzheimer’s
Research has increasingly focused on the science behind olfactory dysfunction as a precursor to Alzheimer’s and similar cognitive impairments. Studies suggest that the neurobiology of smell is closely linked to the brain regions affected early in Alzheimer’s disease. Understanding this relationship may illuminate why a seemingly benign sense, such as smell, can serve as an early warning system for more serious cognitive issues.
By exploring the mechanisms that contribute to olfactory decline, researchers can unlock new paths for investigation into Alzheimer’s. For instance, the Aromha Brain Health Test developed in recent trials highlights the potential for such olfactory-based tests to correlate with cognitive function. This encourages not only further research but also underlines the importance of monitoring olfactory health in assessments of cognitive vigor.
Cultural Considerations in Utilizing Olfactory Tests
Cultural considerations play a pivotal role in how olfactory tests are utilized for Alzheimer’s risk assessment. Given that smell is deeply intertwined with personal and cultural experiences, it is essential to adapt these tests to resonate well with diverse populations. The research conducted, which accommodates both English and Spanish speakers, sets a commendable precedent for inclusivity in cognitive health evaluations.
Tailoring olfactory testing to fit cultural contexts not only enhances engagement but ensures more reliable results. As we acknowledge the diverse backgrounds of individuals affected by Alzheimer’s, adapting assessments accordingly can improve outcomes and lead to more meaningful interpretations of cognitive health. This focus on cultural sensitivity can ultimately strengthen community ties and foster greater awareness about the importance of early detection in neurodegenerative diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the olfactory test for Alzheimer’s and how can it aid in early detection?
The olfactory test for Alzheimer’s involves participants identifying and remembering various odors to assess their olfactory function. This smell test for Alzheimer’s can provide early detection of cognitive impairment and identify individuals at risk of Alzheimer’s long before memory symptoms manifest.
How does olfactory dysfunction relate to Alzheimer’s risk assessment?
Olfactory dysfunction, such as a diminished sense of smell, is recognized as an early warning sign in Alzheimer’s risk assessment. Research indicates that individuals with neurodegenerative diseases often show impaired odor identification and discrimination, making olfactory tests a valuable tool for evaluating Alzheimer’s risk.
Can the olfactory test for Alzheimer’s be performed at home?
Yes, the olfactory test for Alzheimer’s can be conducted at home using simple odor labels placed on a card. This convenient format allows for broader participation while facilitating early detection of cognitive impairment in older adults.
What are the benefits of using a smell test for Alzheimer’s?
The smell test for Alzheimer’s is noninvasive, cost-effective, and can help in early detection of cognitive impairment. By identifying olfactory dysfunction, healthcare providers can assess Alzheimer’s risk and intervene earlier in the progression of the disease.
How effective is the olfactory test for identifying cognitive impairment in older adults?
Research shows that older adults with mild cognitive impairment tend to score lower on olfactory tests compared to their cognitively normal peers, highlighting the test’s effectiveness in identifying early signs of Alzheimer’s and related neurodegenerative diseases.
Is the olfactory test for Alzheimer’s applicable across different languages?
Yes, the olfactory test for Alzheimer’s has demonstrated consistent results across English and Spanish-speaking participants, ensuring its effectiveness in diverse populations and aiding in broader Alzheimer’s risk assessments.
What kind of participants were included in the olfactory test study for Alzheimer’s?
Participants in the olfactory test study included both individuals with subjective cognitive complaints and those diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment, alongside age-matched cognitively normal individuals, all aiding in understanding Alzheimer’s risk and cognitive decline.
What future implications do olfactory tests have for Alzheimer’s research?
Future research may incorporate neuropsychological assessments and longitudinal studies to enhance the predictive power of olfactory tests for assessing Alzheimer’s risk and monitoring cognitive decline over time.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Introduction of Olfactory Tests | Researchers developed at-home olfactory tests to detect Alzheimer’s risk. |
| Methodology | Participants sniff odor labels to assess smell discrimination and memory. |
| Findings | Older adults with cognitive impairment scored lower on the test than normal adults. |
| Future Directions | Further studies could include neuropsychological testing to track cognitive decline. |
| Conclusion | Olfactory testing may predict neurodegenerative disease symptoms in various languages. |
Summary
The Olfactory Test Alzheimer’s is a groundbreaking at-home test that can help identify individuals at risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease years before they show any symptoms. By measuring olfactory function, researchers are exploring a non-invasive, cost-effective method for early detection, which could revolutionize how we approach Alzheimer’s research and treatment. This innovative approach not only shows promise for Alzheimer’s but could also serve as an indicator for other neurodegenerative diseases, emphasizing the importance of further studies to enhance diagnostic capabilities.