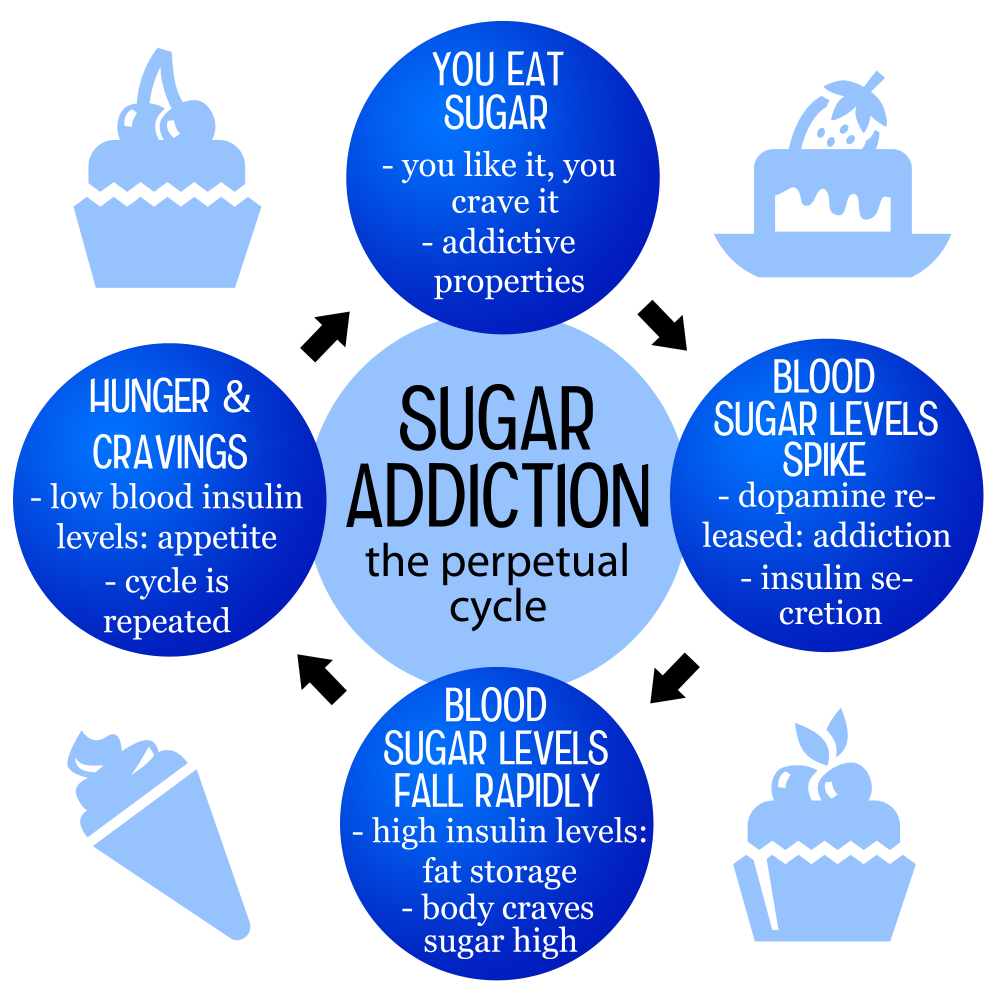
Is sugar addictive? This question has stirred up much debate among nutrition researchers and health professionals, drawing parallels between sugar consumption and the addictive nature of substances like alcohol and nicotine. While some evidence suggests that sugar can trigger cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it hasn’t met clinical criteria for addiction. The health effects of sugar are significant, with high sugar intake leading to various health problems, including obesity and diabetes. Understanding sugar addiction, and its impact on health, is crucial as we navigate our diets filled with processed foods rich in sugar.
The notion of sugar dependence raises vital discussions about our dietary habits and the influence of sweeteners on our well-being. Experts often compare sugar cravings to those associated with addictive substances, highlighting the psychological and physiological responses triggered by sugar consumption. The effects of excessive sugar intake can be profound, influencing not only our physical health but also our mental state, making it essential to consider the implications of trying to eliminate sugar from our diets altogether. While enjoying sweetness is natural, the challenge lies in managing sugar intake effectively to avoid adverse health outcomes. Therefore, exploring alternatives to refined sugars and understanding their roles can provide insights into healthier dietary choices.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
The question, “Is sugar addictive?” often prompts extensive debate among nutritionists and health professionals. While sugar does not meet the clinical definition of addiction like substances such as alcohol or nicotine do, there is compelling evidence that it can foster cravings and compulsive eating patterns. This behavior is influenced largely by the widespread presence of sugar in ultra-processed foods that are designed to be palatable and enticing, making them hard to resist. As people frequently consume products loaded with sugar, the physical craving can feel irresistible, leading to habits that mirror addictive behaviors.
In many cases, the body may react to excessive sugar intake in a way similar to how it responds to addictive substances. For instance, when individuals reduce their sugar consumption abruptly, they can experience withdrawal symptoms like irritability, fatigue, and headaches, akin to those associated with other substances. This blurring of lines between sugar and traditional addictive substances can lead to misunderstandings about how sugar impacts our behavior and health. The relationship with sugar should be managed thoughtfully, emphasizing moderation rather than outright elimination.
The Health Effects of Sugar Consumption
The health effects of sugar cannot be overstated, especially considering that the average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily. Excessive sugar consumption is linked to a range of health problems, such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. When sugar intake surpasses recommended levels—9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women—it can lead to serious long-term health consequences. Understanding the impact of sugar on health is vital for making informed dietary choices that promote overall well-being.
Moreover, the way sugar affects our body involves complex metabolic processes. High sugar consumption can trigger insulin resistance and promote the accumulation of fat around the abdomen, contributing to metabolic syndrome. Additionally, sugary foods often come in the form of processed snacks and drinks that contain unhealthy fats and additives, further exacerbating the health risks. Therefore, it’s essential to be mindful of not just the quantity of sugar consumed, but also the quality of the food sources in our diet.
Managing Sugar Cravings Effectively
Sugar cravings can pose a significant challenge for individuals looking to maintain a healthy lifestyle. It’s not uncommon to feel a powerful urge for sugary treats, especially when stressed or fatigued. Understanding the triggers—whether emotional, environmental, or psychological—can provide insight into how to better manage these cravings. One effective strategy is to gradually reduce sugar intake rather than attempting to eliminate it instantly, which can lead to feelings of deprivation and subsequent bingeing.
Additionally, incorporating nutritious alternatives can help satisfy those cravings without excessive sugar. Foods rich in fiber, proteins, and healthy fats can create a feeling of fullness and diminish the urge for sweets. Simple adjustments, such as choosing whole fruits instead of sugary snacks or drinking water instead of sugary beverages, can make a substantial impact. Ultimately, identifying and addressing the root causes of sugar cravings can enable individuals to take control over their dietary habits.
The Impact of Sugar on Mental Health
Recent studies suggest a significant link between sugar consumption and mental health. High intake of sugar can influence mood fluctuations, leading to increased anxiety and depressive symptoms. Sugar may create a temporary boost in energy, but this is often followed by a crash that can leave individuals feeling lethargic and irritable. This cycle of highs and lows can take a toll on mental well-being, emphasizing the need to be mindful of sugar’s effects on both physical and psychological health.
Moreover, excessive sugar consumption could lead to brain changes that mimic those found in addiction, affecting cognitive functions such as memory and decision-making. It’s essential for people to recognize that what they put into their bodies has vast implications not only for their physical health but also for their mental state. By moderating sugar intake and focusing on balanced nutrition, individuals can improve their overall mental clarity and well-being.
Finding Balance in Sugar Intake
Finding balance in sugar intake is critical for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. While sugar is a natural component found in many foods, excessive consumption of added sugars can lead to adverse health effects. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugars to protect one’s health, but it’s important to recognize that completely eliminating sugar may not be the best approach. Instead, understanding the types of sugars consumed and focusing on whole food sources can ensure that individuals enjoy a variety of flavors in moderation.
Incorporating natural sugars from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet helps satisfy sweet cravings while providing essential nutrients and fiber. By making conscious food choices and reading labels, one can enjoy occasional treats without compromising overall health. This balanced approach can promote a positive relationship with food, allowing for enjoyment while simultaneously safeguarding against the health risks associated with excessive sugar consumption.
The Role of Sugar in Our Diet
Sugar plays a multifaceted role in our diet, serving not just as a sweetener but also as a source of quick energy. Found naturally in many foods, sugar can enhance flavors and improve the enjoyment of meals. However, discerning between natural sugars and added sugars is critical in understanding how we fuel our bodies. While naturally occurring sugars often come with fiber and nutrients, added sugars found in processed foods contribute little more than calories.
To optimize health, it’s crucial to understand sugar’s role in your dietary choices. Many foods that are staples in our diets, such as fruits and dairy products, contain natural sugars that offer various health benefits. Striking a balance by limiting added sugars while embracing natural sources can lead to a nourishing and satisfying diet. This approach not only promotes good health but also enhances enjoyment in eating.
Sugar Consumption Trends and Public Health
Current trends in sugar consumption highlight an urgent public health concern, as rates of sugar intake have skyrocketed over the past few decades. The proliferation of sugary beverages and snacks has led to increased health issues, including obesity and diabetes among all age groups. Understanding these trends is crucial in addressing public health challenges and implementing effective strategies to reduce sugar consumption across communities.
Public health campaigns and initiatives aiming to reduce sugar intake have gained momentum as awareness grows about its detrimental health impacts. Educational efforts focus on encouraging healthier food choices, promoting the reading of nutrition labels, and advocating for policy changes to limit sugar in processed foods. These measures aim to create environments that support healthier eating habits and ultimately reduce the burden of sugar-related health issues.
Sugar and Children: A Growing Concern
The impact of sugar on children’s health is a growing concern among parents and healthcare professionals alike. As children are particularly susceptible to developing a preference for sugary foods, it is essential to monitor and regulate their intake. Excessive sugar consumption can lead to obesity, dental problems, and behavioral issues, necessitating proactive steps to foster healthier eating habits from a young age.
Educating children about nutrition and the potential effects of sugar on their bodies is key to establishing a foundation for lifelong health. Parents can encourage healthier choices by providing a variety of nutritious snacks and modeling balanced eating behavior. Additionally, limiting exposure to sugary products and reinforcing the importance of physical activity can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing sugar-related health problems later in life.
Strategies for Reducing Sugar Intake
For those looking to reduce sugar intake, implementing specific strategies can make the transition smoother and more sustainable. One effective method is to gradually phase out added sugars from the diet, allowing the taste buds to adapt over time. Instead of completely avoiding sugar, replace sugary snacks with healthier alternatives that satisfy cravings while delivering essential nutrients.
Another strategy involves meal prepping and planning to avoid the temptation of convenience foods loaded with added sugars. Preparing meals at home provides better control over ingredients and encourages the incorporation of whole foods that are naturally sweet, like fruits. By staying mindful of hidden sugars in packaged foods and making informed choices, individuals can successfully lower their sugar consumption and enhance their overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can increase cravings and lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance by clinical standards. People may experience withdrawal-like symptoms after reducing sugar intake, but these effects differ significantly in severity compared to substances like alcohol or nicotine.
What are the health effects of sugar consumption?
High sugar consumption can lead to various health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and even less for children to mitigate these health risks.
Why do I experience sugar cravings?
Sugar cravings are attributed to the high palatability of sugary and ultra-processed foods, which can make them addictive-like. These cravings can lead to habitual consumption and may cause withdrawal symptoms when these foods are removed from the diet.
What is the impact of sugar on health overall?
The impact of sugar on health can be significant, especially when consumed in excess. While moderate sugar intake can enhance flavors and enjoyment in food, high levels of added sugar are linked to serious health issues, including metabolic disorders and increased risk of chronic diseases.
How can I reduce my sugar consumption effectively?
To reduce sugar intake, consider gradually cutting back on sugary snacks and drinks rather than eliminating them completely. Read food labels to become more aware of added sugars, and explore healthier alternatives to satisfy sweet cravings.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Sugars and Addictiveness | Despite causing cravings, sugar isn’t classified as addictive like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Food System Context | Ultra-processed foods with high sugar amplify cravings due to their palatability. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Stopping sugar can lead to mild withdrawal symptoms such as headaches or anxiety, but less severe than those from drugs. |
| Moderation Matters | Consuming sugar in moderation is unlikely to have serious health consequences. |
| Awareness of Intake | Monitoring and reducing added sugar consumption gradually is advised. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable debate among nutrition experts. While sugar leads to cravings similar to addictive substances, it is not officially classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. The effects of sugar consumption are notable and often lead to habitual intake, but with awareness and moderation, sugar can be part of a healthy diet. Understanding the context of sugar in today’s ultra-processed food environment highlights the importance of responsible consumption without labeling it as a drug-like substance.