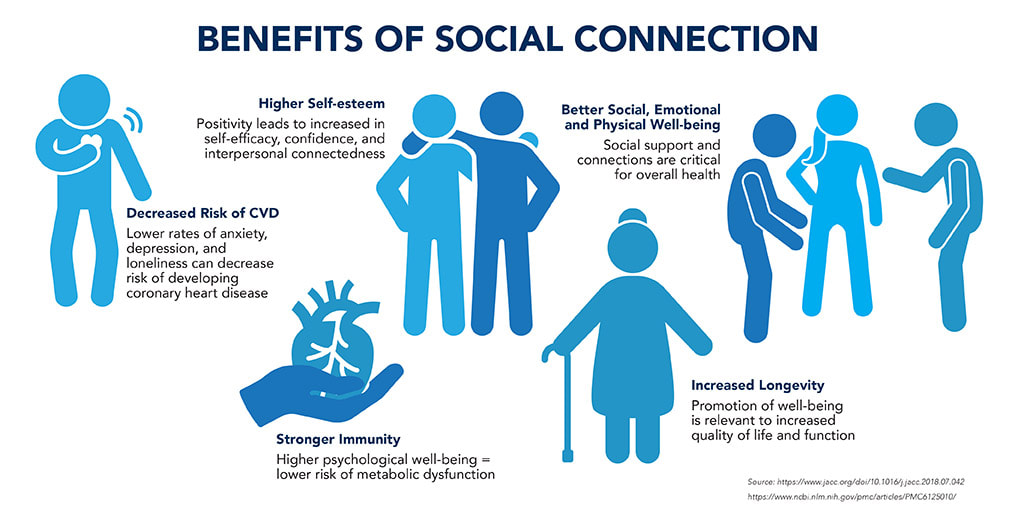
Social connection and health are inextricably linked, as health professionals increasingly recognize the importance of social ties in maintaining well-being. Loneliness and social isolation have been identified by the U.S. Surgeon General as significant public health challenges that warrant serious attention. Recent research delves into the neurological basis of social interaction, shedding light on the brain mechanisms that fuel our innate desire for companionship. Studies indicate that this need for social engagement mirrors the biological drives for food and water, highlighting how vital social behavior is not just for emotional health, but for overall physiological functioning. Understanding the effects of social isolation can also illuminate its severe impacts on mental health, demonstrating the essential role of social interactions in thriving not just among humans but also across social behavior in animals.
The concept of community ties and psychological well-being encompasses various aspects of human experience, wherein our social networks play a critical role in maintaining mental equilibrium. As researchers explore the physiological connections between social relations and human health, new insights emerge about how the dynamics of isolation can affect emotional resilience. The study of companionship needs reveals similarities with fundamental cravings, such as those for nourishment or hydration, providing a compelling perspective on human interactions. By addressing the social aspects of psychological care, we can better understand how integral these relationships are to individual health. This nuanced exploration of interpersonal connections underscores the necessity of fostering deeper bonds within our daily lives.
The Neurological Basis of Social Interaction
Recent research has intensified focus on the neurological foundations that govern social connections, establishing its position as a fundamental human requirement. The hypothalamus, a pivotal brain region, plays an influential role in regulating social behavior, similar to how it monitors hunger or thirst. This study illuminates the intricate neuronal activity that occurs during periods of social isolation and interaction, providing insights into how our brains react to the presence or absence of companionship and the implications it holds for mental health.
By exploring the neurological underpinnings of social needs, researchers have uncovered striking parallels between the drives for social interaction and basic physiological needs. Just as the body signals hunger when food is lacking, the brain activates specific neurons when social engagement is absent. This groundbreaking approach not only enhances our understanding of social behaviors across species but also paves the way for potential therapies aimed at alleviating conditions like depression and anxiety that stem from social isolation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the neurological basis of social interaction and its impact on health?
Recent research has identified that social interaction is encoded in the brain through specific neural circuits that govern social needs, similar to those that regulate hunger and thirst. These findings emphasize the importance of social ties for overall health, highlighting that satisfying social needs is crucial for mental well-being and can influence behaviors in both humans and animals.
How does social isolation affect mental health?
Social isolation can lead to significant mental health challenges, as it deprives individuals of essential social interactions. Studies have shown that prolonged isolation can exacerbate feelings of loneliness, which may worsen conditions such as depression and anxiety. Understanding the impacts of social isolation underscores the necessity of fostering social connections for better mental health.
Why are social ties considered essential for physical and mental health?
Social ties are vital because they serve as a buffer against stress and contribute to a sense of belonging. Engaging in social interactions has been linked to improved mood, lower levels of anxiety, and enhanced overall well-being. The biological mechanisms behind these benefits suggest that social needs are as fundamental as those for food and shelter.
What role does touch play in fulfilling social needs and improving well-being?
Touch plays a crucial role in fulfilling social needs, serving as a powerful method of non-verbal communication and connection. Research indicates that tactile interactions, such as hugging and handshaking, can significantly affect emotional well-being and social behavior. This understanding offers insights into why personal interactions, despite increasing digital communication, remain critical for mental health.
How do animal studies contribute to our understanding of social behavior and health?
Animal studies, particularly with species like mice, reveal fundamental insights into the neurological basis of social behavior and its effects on health. These studies have shown that social needs and behaviors are controlled by specific neurons, reinforcing the idea that social connection is a basic human need akin to food and water. Such research can inform strategies to address social isolation in human populations.
What are the implications of transitioning to digital communication on social health?
As interactions move increasingly towards digital platforms, there is a risk of reduced face-to-face encounters, which are crucial for fulfilling social needs. This shift may lead to a decline in mental health due to the lack of direct human contact, which is essential for emotional and psychological well-being. Understanding the importance of physical presence is vital for addressing these potential health impacts.
How can understanding social connection improve mental health interventions?
By recognizing the neurological basis of social connections, mental health interventions can be better tailored to incorporate social engagement strategies. Programs that encourage social interaction and community building can enhance treatment outcomes for mental health conditions, illustrating the linked nature of social ties and psychological health.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Social Connection as a Basic Need | Health professionals now recognize social interaction as vital as food and shelter. |
| Surgeon General’s Warning | Isolation identified as a major public health issue in 2023. |
| Research Focus | A study in Nature explores the brain mechanisms that drive the need for social interaction. |
| Neuroscientific Findings | Studies find that neurons in the hypothalamus govern social needs similar to hunger and thirst. |
| Negative Feelings and Social Needs | The urge to socialize may be motivated by an avoidance of negative feelings. |
| Experimental Insights | Mice showed altered social behaviors after prolonged isolation, suggesting profound psychological impacts. |
| Importance of Touch | Touch is critical for social fulfillment, indicating its importance in human interactions. |
| Implications of Findings | Understanding social needs can enhance mental health strategies and improve human relationships. |
Summary
Social connection and health are intricately linked, as research increasingly highlights the fundamental need for social interaction similar to basic physiological needs like hunger and thirst. This understanding emphasizes that fostering social ties is crucial not only for individual well-being but also for broader public health. By exploring the neuroscience behind social behavior, we can better address issues related to mental health and improve our interpersonal relationships in a world that often isolates us.