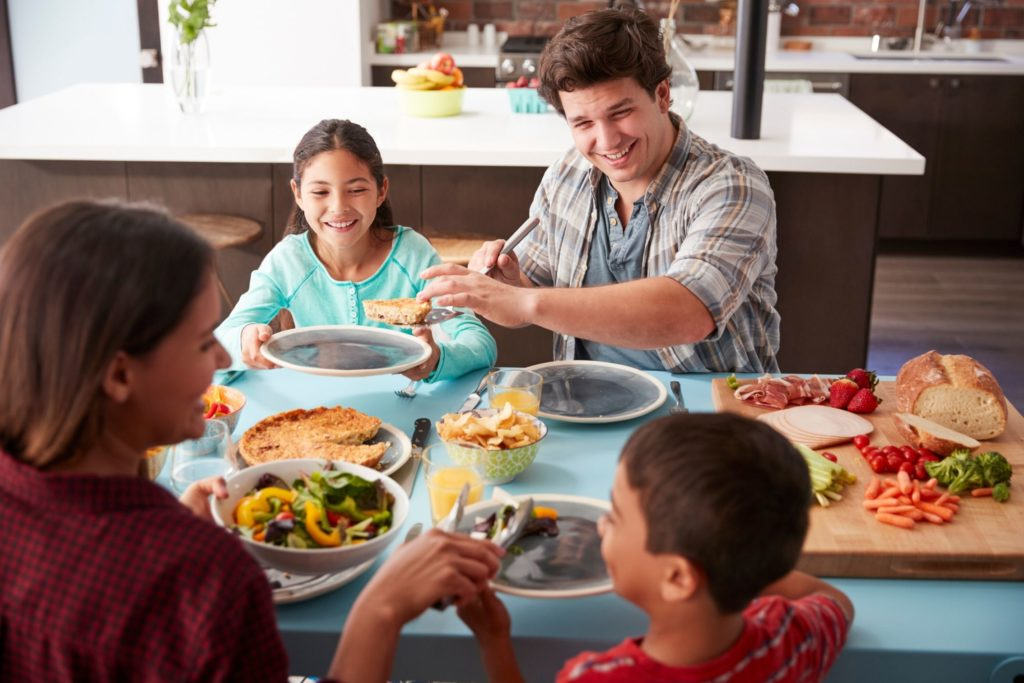
Shared meals and happiness often go hand in hand, embodying the essence of connection and joy that stems from breaking bread together. Recent studies have unveiled a profound correlation between the act of dining with others and enhanced well-being, suggesting that shared meals might be more indicative of overall life satisfaction than traditional markers like income. The benefits of social dining extend beyond mere nourishment; they play a crucial role in emotional health, fostering positive interactions that uplift spirits and strengthen relationships. As individuals increasingly dine alone, the question arises: how can we harness the impact of meals on well-being to promote a more connected society? By recognizing the happiness through shared meals, we can shift our focus towards creating more communal dining experiences that enrich our lives and those around us.
Gathering around a table for a meal is not just about satisfying hunger; it represents an opportunity for companionship and emotional enrichment. The joy derived from eating together transcends cultures, acting as a universal language that fosters bonds and nurtures mental health. As various studies illuminate the social dining benefits, they reveal the integral relationship between mealtime interactions and emotional wellness. Whether it’s a family dinner or a gathering with friends, these shared moments contribute purposefully to our psychological well-being. By understanding the significance of communal dining experiences, we can actively seek ways to incorporate more of these joyous occasions into our lives, enhancing our overall happiness.
The Joy of Shared Meals: A Pathway to Happiness
Shared meals have long been regarded as a cornerstone of human connection and social bonding. The notion that dining together fosters happiness is supported by research indicating that individuals who frequently share meals experience greater satisfaction in their lives. This phenomena transcends socio-economic status, age, and diverse cultural backgrounds, suggesting that the emotional and psychological benefits of shared meals are universal. For instance, a study highlighted in the World Happiness Report found that the frequency of shared meals can predict levels of happiness just as reliably as income or job status.
Moreover, the act of coming together over a meal provides an opportunity for family and friends to build and strengthen relationships. These connections become integral in cultivating a supportive environment, which is fundamental for emotional health. By participating in social dining, individuals engage in meaningful conversations, share experiences, and create memories—all of which contribute significantly to their overall sense of well-being. Thus, the happiness derived from shared meals extends far beyond the meal itself, impacting emotional resilience and social fulfillment.
The Impact of Social Dining on Emotional Health
The relationship between social dining and emotional health has become increasingly significant in an isolating world. Numerous studies reveal that people who regularly engage in shared meals enjoy enhanced emotional health and lower levels of loneliness. The feeling of being connected to others during mealtime creates a sense of community, which is vital for mental wellness. As meals serve as a social gathering point, they can help combat feelings of isolation and foster a sense of belonging.
Furthermore, the psychological benefits of shared dining extend to enhancing one’s mood and reducing stress. Engaging with friends or family over a meal is not only about the food but also about the laughter, companionship, and support that accompany it. Such interactions are crucial for emotional balance and can buffer against depression and anxiety. In today’s fast-paced society where solitary dining is on the rise, noticing the impact of meals on our emotional health calls for a resurgence in prioritizing social dining.
Exploring the Correlation Between Meals and Well-Being
Exploring the correlation between shared meals and overall well-being reveals much about human social behavior. Research has identified that the frequency of shared meals among individuals correlates strongly with their self-reported levels of happiness. Such findings indicate that social dining could serve as a valuable metric for assessing well-being, potentially even surpassing traditional measures like income. With the ongoing decline in communal dining experiences, especially in the United States, the implications of this research bear significant weight, particularly concerning mental health and social isolation.
Moreover, one fascinating aspect of this correlation is that it raises questions about causation. Are happier individuals more likely to share meals, or does the act of sharing meals contribute to an increase in happiness? While definitive answers remain elusive, the inquiry itself emphasizes the need for a deeper understanding of social interactions and their impacts on mental health. As researchers continue to delve into this area, fostering environments that encourage shared meals could become a practical approach to improving community well-being.
The Role of Societal Trends in Mealtime Dynamics
Current societal trends show a disturbing increase in solitary dining. Reports indicate that a significant portion of the population is opting to dine alone, with statistics highlighting a 53 percent increase in solitary meals over the past two decades. This shift poses concerns about the broader implications for social health and highlights the need for communities and policymakers to address these trends. Understanding these dynamics can provide insights into the factors contributing to social isolation and emotional decline.
As single dining becomes more prevalent, it underscores a potential crisis in social connectivity. Communities need to recognize how vital shared meals are for creating social bonds. Bringing back communal dining experiences could serve as an effective strategy for enhancing emotional health and overall happiness in communities. Encouraging regular family dinners, community potlucks, and public dining events could help reverse the rising trend of isolation, enhancing not only individual well-being but also enriching the community as a whole.
Investing in Shared Meals: A Community Approach
Investing in initiatives that promote shared meals could profoundly impact community health and social interaction. Programs aimed at facilitating communal dining experiences can offer productive avenues for engagement, fostering bonds that enrich emotional health. This could include the establishment of community kitchens, neighborhood dinner clubs, or public events celebrating food and fellowship. Such investments not only enhance individual relationships but contribute to a more cohesive community fabric.
By prioritizing the practice of shared meals, communities can cultivate environments where social interactions thrive. When individuals gather to share food, they’re not just feeding their bodies—they’re feeding their spirits. Addressing the trend of solitary dining through community-driven initiatives can lead to healthier, more connected populations. As we move forward, understanding the role of shared meals in building happiness offers actionable pathways toward more vibrant, supportive communities.
Understanding the Science Behind Mealtime Interaction
The science behind mealtime interactions reveals complex relationships between food, emotion, and social dynamics. Research has shown that sharing a meal can release oxytocin, a hormone associated with bonding and well-being. This suggests that the very act of dining together can promote feelings of trust and belonging. Moreover, mealtime conversations often lead to the exchange of ideas and support, further strengthening social ties.
Understanding these scientific principles reinforces the importance of prioritizing shared meals in everyday life. As people increasingly turn to solitary dining, it’s crucial to recognize the benefits lost when meals are taken alone. By facilitating opportunities for shared dining, communities can harness the power of food to enhance emotional health, build relationships, and create a stronger social network.
Shared Meals as a Source of Happiness
Shared meals are not just about sustenance; they are a profound source of happiness that stems from social connection. Engaging in communal dining creates opportunities for laughter, conversation, and emotional support, all of which contribute to a person’s happiness. The atmosphere of shared dining often leads to joyful experiences that create lasting memories, enhancing the sense of fulfillment and belonging within social groups.
Moreover, the happiness derived from shared meals transcends the immediate event, fostering ongoing connections that strengthen over time. When individuals regularly gather to share meals, they are effectively building a supportive community that enhances emotional health and resilience. Thus, prioritizing shared meals as a cultural norm can lead to healthier, happier societies where individuals feel more connected and supported.
Encouraging Communal Dining: Strategies for Improvement
To encourage communal dining, strategic initiatives must be implemented at both community and individual levels. Promoting public awareness about the benefits of shared meals can motivate people to prioritize dining together. This can be achieved through community events, school programs, and workshops that focus on cooking and eating as a collective experience. Organizations can play a pivotal role by hosting regular community meals, potlucks, or themed dining nights that bring people together.
Additionally, simplifying the logistics of communal dining can make it more accessible. Initiatives such as community kitchens or shared dining spaces can alleviate barriers to participation. As more people engage in these communal activities, the ripple effect may lead to enhanced emotional well-being across communities. Investing in the culture of shared meals holds the potential to create a happier society where connections flourish and emotional health is prioritized.
Future Research Directions: Meal Sharing and Mental Health
Future research directions focusing on the link between meal sharing and mental health will be crucial in understanding the deeper implications of social dining. Investigating whether increased shared meals can lead to measurable improvements in emotional health will provide valuable insights for policymakers and community leaders. Identifying specific elements of shared dining—such as the frequency, duration, and nature of mealtime interactions—could yield actionable data to support community initiatives aimed at enhancing well-being.
Moreover, understanding the demographic differences in social dining habits may help target interventions more effectively. For instance, engaging younger populations who are increasingly dining alone could involve tailored outreach strategies that emphasize the benefits of shared meals. By grounding future research in empirical evidence, we can develop stronger frameworks for promoting happiness through social dining, ultimately fostering healthier and more connected communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do shared meals promote happiness in individuals?
Shared meals have been linked to increased levels of happiness and well-being. Studies indicate that dining with others enhances social connections, promotes joy, and fosters positive emotions. This collective experience can create a sense of belonging and fulfillment, making it a vital aspect of emotional health.
What are the social dining benefits that contribute to emotional health?
The benefits of social dining include improved communication, stronger relationships, and emotional support. When people share meals, they engage in conversations that strengthen bonds, contribute to a sense of community, and ultimately boost their happiness and overall well-being.
Is there evidence of the impact of meals on well-being?
Yes, research shows a clear correlation between shared meals and well-being. Individuals who dine with others experience greater life satisfaction and emotional stability, suggesting that communal eating is as vital to happiness as traditional measures like income or employment status.
Can mealtime experiences enhance emotional health and happiness?
Absolutely! Positive mealtime experiences can enhance emotional health by providing an opportunity for family bonding, laughter, and the sharing of stories. These interactions during meals contribute to happiness by reinforcing social ties and creating lasting memories.
What role does shared dining play in improving overall happiness?
Shared dining plays a crucial role in improving happiness by actively engaging individuals in social interactions. The consistent practice of sharing meals leads to a supportive environment that fosters joy, reduces feelings of loneliness, and enhances emotional connections with others.
Why is it important to promote shared meals in our communities for better well-being?
Promoting shared meals within communities is essential for enhancing social cohesion and individual well-being. As studies suggest, increasing the frequency of shared dining not only boosts happiness but also helps combat social isolation, which is increasingly prevalent in today’s society.
What factors make shared meals a reliable indicator of happiness?
Shared meals are a reliable indicator of happiness because they reflect social engagement and connection. Research has shown that higher frequency of communal dining correlates with positive emotional states across diverse demographics, making it a straightforward and impactful measure of well-being.
How can we increase the frequency of shared meals to improve happiness levels?
To increase shared meals, individuals can organize regular family dinners, host potlucks with friends, or engage in community dining events. Encouraging a culture of shared meals can significantly enhance social bonds and contribute positively to overall happiness.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Shared Meals vs. Income | Sharing meals may be a more reliable indicator of well-being than income or employment status. |
| Increased Loneliness | Roughly 1 in 4 Americans reported eating all meals alone, a 53% increase since 2003. |
| Impact Across Demographics | The correlation between shared meals and happiness is observed across all ages, genders, and cultures. |
| Measurement of Happiness | The study suggests that the number of shared meals is a clearer indicator of happiness compared to income. |
| Future Research | Researchers aim to explore if sharing meals actually causes increased happiness. |
| Policy Implications | Encouraging shared meals could serve as a policy intervention to increase well-being and combat social isolation. |
Summary
Shared meals and happiness are intricately linked, as research suggests that the frequency of dining with others plays a significant role in overall well-being. The correlation between shared meals and satisfaction with life indicates that fostering communal eating experiences may improve happiness levels across various demographics. As social isolation increases, it becomes crucial for individuals and policymakers to prioritize shared meals as a means to enhance community connections and promote mental well-being. Understanding this relationship can provide valuable insights into fostering a happier society.