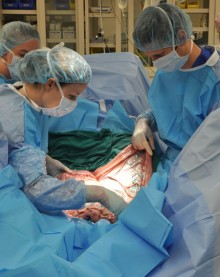
CALEC surgery, or cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell transplantation, represents a groundbreaking advancement in the field of ocular repair and regeneration. Developed at Mass Eye and Ear, this innovative procedure utilizes stem cell therapy to restore the cornea’s surface, showing remarkable effectiveness in treating corneal damage previously deemed untreatable. The procedure involves harvesting limbal epithelial cells from a healthy eye, expanding them into grafts, and transplanting these into the damaged eye to combat the risk of blindness. With an impressive success rate exceeding 90%, CALEC surgery is transforming lives by alleviating chronic pain and restoring vision for individuals affected by severe corneal injuries. As a result, this surgery is not only a beacon of hope but also a significant leap forward in eye repair procedures that harness the power of regenerative medicine.
Referred to as cultivated limbal epithelial cell therapy, this pioneering technique is revolutionizing treatment options for patients suffering from corneal damage. By leveraging the regenerative capabilities of stem cells, this approach focuses on rebuilding the eye’s essential surface tissue. The procedure is notable for its ability to address debilitating conditions that can lead to vision impairment or blindness, offering newfound hope to those impacted by severe ocular injuries. As research progresses, efforts are underway to expand the accessibility of this transformative treatment to a broader patient base, ensuring that more individuals can benefit from this cutting-edge eye repair solution.
Understanding CALEC Surgery and Its Impact
CALEC surgery, which stands for cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells, represents a groundbreaking advancement in eye repair procedures. This technique involves harvesting stem cells from a healthy eye, which are then expanded into a suitable graft to treat corneal damage. The process significantly benefits patients who suffer from corneal injuries that have previously led to the loss of vision or chronic pain. By restoring the cornea’s surface, CALEC surgeries offer hope to those facing blindness due to severe limbal epithelial cell deficiency.
During the surgical procedure, specialized teams meticulously transplant the grafts into damaged eyes, showcasing a high success rate that exceeds 90%. These successes underline the effectiveness of stem cell therapy in transforming eye repair methodologies, providing new levels of restoration for previously untreatable conditions. As clinical trials continue to expand, CALEC surgery could soon become a standard procedure in ophthalmic medicine, helping to normalize life for patients affected by corneal damage.
The Role of Stem Cell Therapy in Eye Repair
Stem cell therapy plays a vital role in the landscape of eye repair, particularly for conditions that lead to corneal damage. By utilizing cultivated limbal epithelial cells, researchers are able to regenerate essential parts of the cornea, substantially reducing the risk of blindness. This innovative approach not only focuses on restoration but also emphasizes long-term recovery through the sustainable healing of the eye’s surface.
The clinical trials at Mass Eye and Ear provide compelling evidence for the efficacy of this therapy. Participants in these trials showed remarkable improvements, with complete restoration of the cornea in up to 50% of cases after just three months. Such findings not only highlight the potential of stem cell therapy in treating corneal injuries but also pave the way for future advancements in blindness treatment. As ongoing research unfolds, the applications of stem cell therapy for broader ophthalmic conditions are becoming increasingly promising.
Corneal Damage Treatment: Innovative Approaches
Corneal damage can stem from several sources, including infections and chemical burns, leading to debilitating consequences for vision. Traditional methods, including corneal transplants, often pose risks and complications, reinforcing the need for innovative treatments like CALEC surgery. This technique provides a sustainable solution by leveraging the body’s own stem cells to repair and regenerate the cornea effectively.
Through rigorous research and development, the Mass Eye and Ear team is pioneering methods that hold the potential to transform corneal damage treatment. The trials indicate that stem cell-derived grafts can not only restore vision but do so with minimal complications. This level of safety and effectiveness signifies a critical shift in how corneal injuries are treated, offering patients a chance at improved quality of life without the ongoing pain associated with untreated corneal damage.
Limbal Epithelial Cells: The Key to Recovery
Limbal epithelial cells play a crucial role in maintaining the health and integrity of the cornea. When injury depletes these cells, the cornea can no longer regenerate properly, leading to significant damage and vision loss. Understanding the function of limbal stem cells allows researchers to harness their regenerative capabilities. The CALEC procedure focuses on extracting and cultivating these cells to rehabilitate the injured area of the cornea.
Research has shown that restoring these vital cells can bring about a dramatic recovery in patients who have suffered serious corneal injuries. With the successful application of CALEC surgery, doctors can now provide a reliable treatment option that not only restores vision but also alleviates chronic pain associated with damaged corneas. This innovation positions limbal epithelial cells as a focal point of treatment in ophthalmology.
Future Directions in Eye Repair Technology
As research into CALEC surgeries and stem cell therapy progresses, the future of eye repair technology is poised for significant advancements. The integration of innovative techniques opens up new pathways for treating a variety of eye conditions that lead to blindness. The increasing efficacy observed in clinical trials marks an exciting new era in regenerative medicine, where patients previously considered untreatable can now receive viable options.
Looking ahead, the goal is to refine these methodologies and broaden their availability to diverse patient populations. The hope is to establish allogeneic methods, allowing for treatment across patients with bilateral corneal damage. The commitment to ongoing research will be vital in ensuring that these life-changing therapies reach those who need them most.
Safety and Efficacy of CALEC Surgery
Patient safety and treatment efficacy are paramount in any surgical procedure, particularly in innovative approaches like CALEC surgery. Clinical trials have indicated a robust safety profile for this treatment, with minimal adverse events reported. The rigorous monitoring of participants post-transplant has shown that complications are rare, and most recoveries are swift and uneventful.
The focus on safety not only enhances confidence among clinicians and patients but also sets a precedent for future stem cell therapies. As the body of evidence supporting CALEC surgery grows, it strengthens the argument for its adoption in clinical practice, with the potential for a substantial impact on the lives of those dealing with chronic ocular conditions.
Challenges in Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency Treatments
Despite the promising results of CALEC surgery, there are inherent challenges that need to be addressed, particularly the limitations regarding eligibility for treatment. For the procedure to be viable, patients must possess one healthy eye to serve as a stem cell donor, which can restrict access for many individuals suffering from bilateral corneal diseases.
This challenge underscores the necessity for ongoing research aimed at developing allogeneic approaches, which could utilize stem cells from cadaveric sources. Such advancements would not only expand the pool of eligible patients but could significantly revolutionize how congenital and acquired limbic stem cell deficiencies are treated.
The Importance of Clinical Trials in Advancing Eye Care
Clinical trials are the backbone of medical advancement, providing the necessary framework to test the efficacy and safety of emerging therapies. In the context of CALEC surgery, rigorous trials have demonstrated the transformative potential of stem cell therapy in treating corneal damage. As these studies unveil positive results, they encourage further exploration and development, bringing innovative solutions to the forefront of ophthalmic care.
Moreover, the inclusion of diverse patient populations in clinical trials is essential for ensuring that new treatments are effective across various demographics. Future studies must continue to prioritize inclusivity to fully understand the breadth of CALEC surgery’s impact on different patient groups and, ultimately, improve eye care for all.
Collaborative Research and Its Impact on Treatment Development
Collaboration among institutions plays a pivotal role in accelerating the development of effective treatments for eye diseases. The partnership between Mass Eye and Ear, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and Boston Children’s Hospital exemplifies how multidisciplinary teams can enhance research outcomes in the field of regenerative medicine. By combining expertise, these institutions are making strides towards innovative solutions like CALEC surgery.
Such collaboration not only enhances the quality of research but also broadens the scope of patient care. By sharing findings and resources, teams can refine their approaches to stem cell therapy and transplantation, ensuring that future iterations of CALEC and similar treatments are safer and more effective. This cooperative spirit is essential for the continued evolution of eye repair technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is CALEC surgery and how does it relate to stem cell therapy?
CALEC surgery, which stands for cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell surgery, is an innovative procedure that employs stem cell therapy to treat severe corneal damage. By extracting and expanding limbal epithelial cells from a healthy eye, surgeons can create a graft to restore the damaged cornea. This technique has shown over 90% effectiveness in helping patients with blinding corneal injuries.
How does CALEC surgery treat corneal damage?
CALEC surgery treats corneal damage by utilizing stem cells harvested from a healthy eye. These limbal epithelial cells are cultured to create a tissue graft that is then transplanted into the damaged eye. This process specifically targets limbal stem cell deficiency, enabling the regeneration of the cornea’s surface and restoring vision in previously untreatable cases.
What are the success rates of CALEC surgery for blindness treatment?
In clinical trials, CALEC surgery has demonstrated impressive success rates: 50% of participants achieved complete corneal restoration at three months, with success rates rising to 79% and 77% at 12-month and 18-month follow-ups, respectively. Overall, the procedure has shown to have a 92% effectiveness rate in restoring the corneal surface for patients with severe damage.
Is CALEC surgery safe for treating eye repair procedures?
Yes, CALEC surgery has exhibited a high safety profile with no serious complications reported in either the donor or recipient eyes. While there were minor adverse events, such as a bacterial infection in one participant, these complications were manageable and resolved quickly.
Who can benefit from CALEC surgery and its stem cell therapy?
Patients suffering from blinding corneal injuries and limbal stem cell deficiency are the primary beneficiaries of CALEC surgery and its stem cell therapy. This innovative treatment gives hope to individuals who have limited options for vision restoration due to severe corneal damage.
What is the future of CALEC surgery in terms of availability and research?
Currently, CALEC surgery remains experimental and is not widely available. However, ongoing research aims to conduct larger trials and eventually submit the procedure for federal approval. The hope is to broaden access to this potentially life-changing treatment for patients with corneal damage in both eyes in the future.
How does CALEC surgery differ from traditional corneal transplant procedures?
Unlike traditional corneal transplants, which require a donor cornea, CALEC surgery uses the patient’s own limbal epithelial cells cultivated into a graft. This minimizes the risk of rejection and provides a tailored approach to treating corneal damage that was previously deemed untreatable.
What are the steps involved in the CALEC surgery process?
The CALEC surgery process involves extracting limbal epithelial cells from a healthy eye through a biopsy, expanding these cells to create a graft, and then surgically transplanting the graft into the damaged eye. This innovative method takes approximately two to three weeks to prepare the graft before the surgical intervention.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| First CALEC Surgery | Performed by Ula Jurkunas at Mass Eye and Ear. |
| Procedure Overview | Involves extracting stem cells from a healthy eye, expanding them into a graft, and transplanting into the damaged eye. |
| Trial Results | Over 90% effectiveness in restoring corneal surface after treatment in 14 patients. |
| Safety Profile | No serious complications; one minor infection reported, resolved quickly. |
| Future Directions | Plans to develop an allogeneic method for patients with bilateral eye damage. |
| Trial Approval | Gained approval from the FDA and was the first human study funded by the National Eye Institute. |
Summary
CALEC surgery represents a groundbreaking advancement in ophthalmic treatment, demonstrating a viable approach for patients suffering from debilitating corneal damage. The innovative use of stem cells provides hope for restoring vision that was previously deemed irreparable, marking a transformative step in ocular medicine. As further studies are planned to broaden patient eligibility and enhance treatment efficacy, CALEC surgery stands on the brink of potentially revolutionizing eye care.