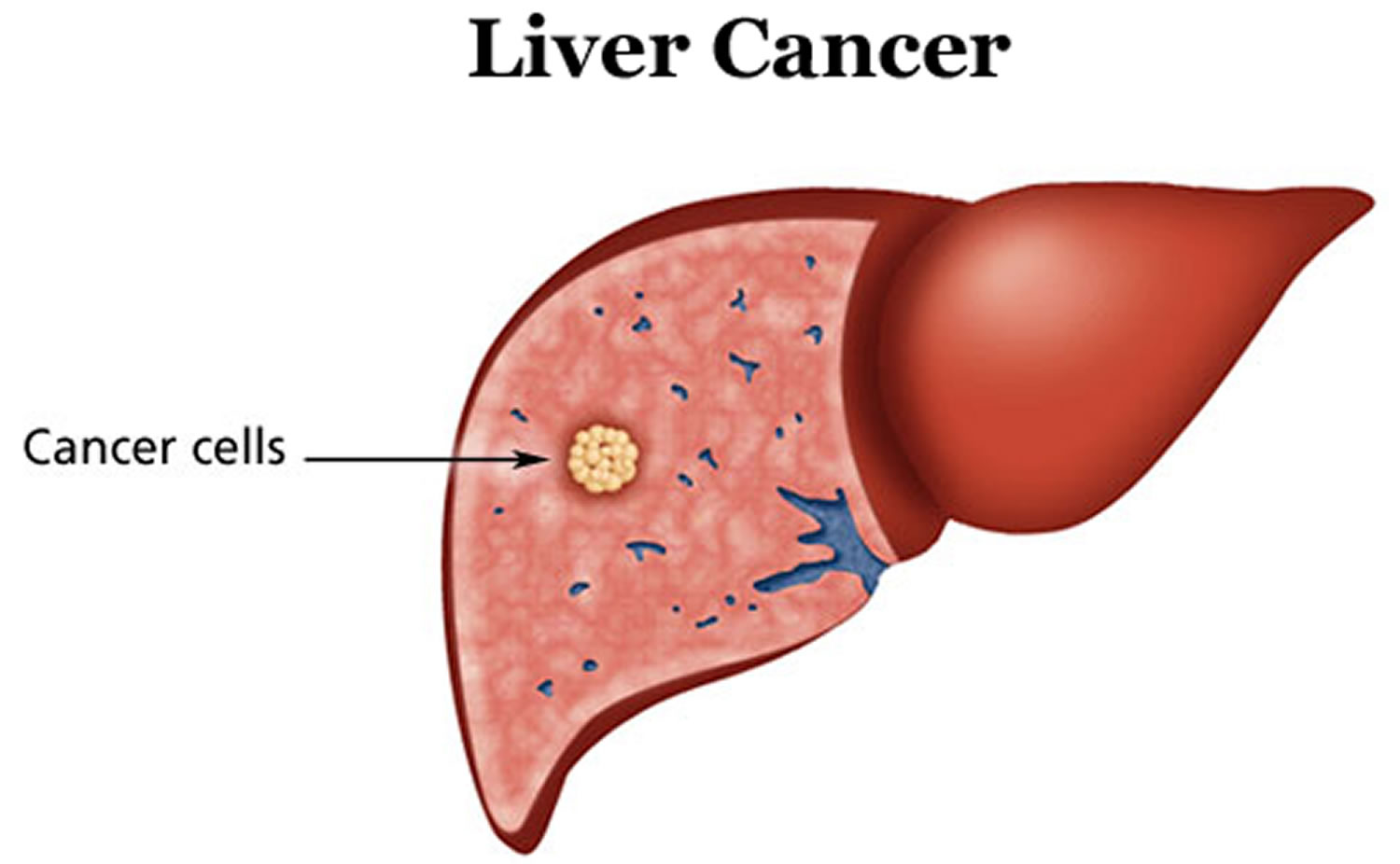
Liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is a dire health concern linked to an imbalance in bile acids produced by the liver. Recent studies highlight how disruptions in bile acid metabolism can not only lead to liver disease but also provide crucial insights into potential therapeutic interventions for liver cancer. By exploring the role of the YAP protein and the FXR receptor, researchers are uncovering the intricate mechanisms underlying liver cancer progression and the pathophysiology of liver disease. This research is vital as it opens the door to novel approaches aimed at restoring metabolic balance in the liver, which could significantly alter the prognosis for patients facing this aggressive form of cancer. Understanding these connections will enhance future treatment strategies, ultimately contributing to better health outcomes for those affected by liver cancer.
Hepatic malignancies, particularly the most prevalent type known as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), represent a significant challenge in the medical field. Research indicates that an imbalance in bile salts and their metabolic pathways can trigger serious liver conditions, leading to cancer development. Investigations into the YAP signaling pathway and the FXR nuclear receptor are crucial for elucidating how abnormal bile acid regulation might contribute to tumorigenesis in the liver. As scholars deepen their understanding of this metabolic disorder, they uncover potential targets for pharmacological intervention that could alter the trajectory of liver-related diseases. Addressing these key factors is essential for devising effective strategies against liver cancer and improving overall liver health.
Understanding Bile Acid Metabolism and Liver Health
Bile acid metabolism is a complex biological process that plays a crucial role in maintaining liver health. The liver is responsible for producing bile acids, which not only aid in the digestion of fats but also help regulate lipid metabolism and glucose homeostasis. When this balance is disrupted, it can lead to diseases such as liver inflammation, fibrosis, and ultimately, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Understanding the finely-tuned regulation of bile acid metabolism is vital to unveil new therapeutic strategies for liver diseases.
Moreover, the role of key receptors, such as the FXR receptor, cannot be overstated. FXR is essential for managing bile acid synthesis and transport within the liver. Dysregulation of FXR has been linked to adverse liver conditions, emphasizing the need for research focused on how this receptor can be targeted to restore balance in bile acid levels and improve outcomes for patients suffering from liver diseases.
The Link between YAP Protein and Liver Cancer
The YAP protein has emerged as a significant player in the context of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent studies show that YAP not only contributes to cell growth and proliferation but also plays an unexpected role by repressing the FXR receptor. This inhibition can lead to an accumulation of bile acids, creating a hostile environment that promotes liver damage and tumor formation. Understanding how YAP modulates these pathways can provide insights into potential therapeutic interventions that could mitigate liver cancer progression.
Activating the signaling pathways that counter YAP’s repressive effects on FXR may offer a promising strategy in treating liver cancers. By enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid detoxification and excretion, researchers can potentially disrupt the cascade that leads to hepatic inflammation and cancer. Such insights are vital for developing pharmacological strategies aimed at improving liver health and reducing cancer risk.
Potential Interventions for Liver Disease Prevention
Considering the detrimental impact of bile acid imbalance on liver health, exploring potential interventions is critical. Interventions may include pharmacological agents that activate the FXR receptor, which has shown promise in restoring bile acid homeostasis. Additionally, dietary modifications that promote bile acid secretion and proper liver function can be considered as complementary approaches to pharmacotherapy. Leveraging lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet rich in fiber and low in saturated fats, can contribute significantly to liver disease prevention.
Furthermore, ongoing research into the role of bile acids in metabolic regulation may unveil new preventative measures against liver diseases. Public health initiatives aimed at raising awareness about liver health and advocating for early screening could also play a crucial role in tackling the rising incidence of liver cancer. By combining research efforts with community education, we can work toward a future with reduced risks of liver diseases.
Research Insights on Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Research into hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has highlighted the importance of molecular mechanisms underlying liver cancer development. Studies have found that various signaling pathways, particularly those involving bile acid metabolism and the Hippo/YAP pathway, are intricately linked to HCC progression. Targeting these pathways could lead to innovative treatment modalities and improve patient outcomes. The exploration of how bile acids affect gene expression and cellular signaling continues to be a promising area of study in oncology.
Additionally, understanding how specific proteins, such as YAP, interact with bile acid receptors like FXR provides critical insights into the pathophysiology of liver cancer. The discovery of potential therapeutic targets within these pathways not only enhances our understanding of cancer biology but also paves the way for novel interventions that could significantly hinder tumor growth and metastasis in liver cancer patients.
The Role of Cell Signaling in Liver Disease
Cell signaling plays an indispensable role in regulating liver physiology and health. Key pathways, such as the Hippo/YAP signaling axis, are essential for maintaining cellular balance in the liver. Disruption of these signaling pathways can lead to the onset of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Research focusing on the intricate network of cell signaling mechanisms holds the key to understanding how to prevent and treat liver diseases effectively.
By investigating how signaling pathways influence bile acid metabolism and liver function, researchers can identify critical checkpoints for intervention. Therapies aimed at restoring proper cell signaling in liver cells can help in mitigating the effects of liver injury and reducing cancer risk. Therefore, ongoing research in this area is paramount for developing targeted therapies that can effectively address the complex challenges associated with liver diseases.
Molecular Targets for Liver Cancer Treatment
Identifying molecular targets for liver cancer treatment is vital in the fight against hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The recent study highlighting the role of YAP protein in regulating bile acid metabolism provides a compelling case for targeting this player in liver cancer therapy. By inhibiting YAP’s repressive function on the FXR receptor, researchers may develop treatment options that alleviate liver injury and curb cancer cell proliferation, thereby offering hope for patients diagnosed with liver cancers.
Moreover, the exploration of other signaling pathways involved in liver pathology, such as those mediated by bile acids and FXR, introduces additional targets for therapeutic development. Collaborative efforts amongst researchers can facilitate the discovery of novel drugs capable of altering bile acid signaling dynamics, which would ultimately lead to improved treatment responses for liver cancer patients and those suffering from liver disease.
Innovations in Liver Cancer Research
Innovations in liver cancer research have been propelled by studies focusing on cellular mechanisms, such as those involving bile acid metabolism. The exploration of how various signaling pathways intersect offers a promising frontier for therapeutic strategies aimed at liver cancer. The increased understanding of the molecular underpinnings of liver diseases may lead to groundbreaking treatments and advancements in patient care.
As research continues to unfold, the development of experimental therapies targeting specific receptors like FXR and proteins such as YAP could revolutionize the landscape of liver cancer treatment. Ongoing investigations into the effects of bile acids on cellular growth and differentiation could lead to novel approaches in managing not just hepatocellular carcinoma, but broader aspects of liver health and disease.
The Impact of Diet on Bile Acid Regulation
Diet plays a significant role in bile acid regulation and subsequently impacts liver health. Consumption of high-fiber foods can enhance bile acid secretion and promote a healthy gut microbiota, contributing to the prevention of liver disease. By adopting a diet that supports healthy bile acid metabolism, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma and other liver-related conditions.
Moreover, avoiding foods high in saturated fats and sugar can prevent bile acid dysregulation, thereby reducing the likelihood of liver inflammation and fibrosis. Public health initiatives should emphasize dietary education as a crucial element in promoting liver health and preventing liver diseases. By encouraging healthier eating habits, we can collectively contribute to improving liver health on a population level.
Community Engagement in Liver Health Awareness
Community engagement is vital in fostering awareness about liver health and the risks of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Education initiatives aimed at informing the public about the importance of liver health, the role of bile acids, and lifestyle factors can empower individuals to make informed choices. Community workshops, seminars, and outreach programs can spread knowledge regarding early detection and prevention strategies.
Additionally, creating support networks for individuals affected by liver disease can provide essential resources and information. By building a community that prioritizes liver health, we can collectively raise awareness and encourage proactive management of liver conditions, ultimately leading to a healthier society.
The Future of Liver Cancer Therapeutics
As research continues to unveil the complexities of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the future of liver cancer therapeutics is promising. The identification of molecular pathways involved in bile acid metabolism and cellular signaling—particularly those related to YAP and FXR—provides a solid foundation for developing innovative treatment approaches. With advancements in molecular biology and genetics, targeted therapies can be designed to disrupt the mechanisms that facilitate tumor growth.
Moreover, ongoing clinical trials focusing on novel pharmacological agents that enhance FXR function or inhibit YAP’s repressive action may yield groundbreaking results. The integration of multidisciplinary approaches—combining pharmacology, nutrition, and lifestyle modifications—can further improve therapeutic outcomes for individuals diagnosed with liver cancer. The collective effort of researchers and clinicians stands to significantly enhance liver cancer care in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between bile acid metabolism and liver cancer?
Bile acid metabolism plays a crucial role in liver health, and an imbalance can lead to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. Disruptions in bile acid regulation can cause liver injury and inflammation, leading to cancer development.
How does the YAP protein influence the progression of liver cancer?
The YAP protein contributes to liver cancer progression by regulating bile acid metabolism. Rather than promoting growth directly, YAP inhibits the function of the FXR receptor, crucial for bile acid homeostasis, leading to increased bile acid levels in the liver, which can result in inflammation and fibrosis, ultimately increasing the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
What role does the FXR receptor play in liver disease and cancer prevention?
The FXR receptor is vital for maintaining bile acid homeostasis in the liver. Enhancing FXR function can help prevent liver disease by reducing excessive bile acid production, thus potentially decreasing the risk of developing liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma.
Can liver cancer be triggered by bile acid accumulation?
Yes, liver cancer can be triggered by bile acid accumulation. When bile acid metabolism is disrupted, it leads to excessive bile acids in the liver, causing inflammation and fibrosis, which are significant risk factors for developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
What are potential treatment strategies for liver cancer related to bile acid metabolism?
Potential treatments for liver cancer may include strategies to enhance FXR receptor function or promote bile acid excretion. Research indicates that activating FXR or inhibiting YAP’s repressive activity can reduce liver damage and slow down cancer progression.
How do signaling pathways influence liver cancer development?
Signaling pathways, especially the Hippo/YAP pathway, influence liver cancer by regulating processes such as cell growth and bile acid metabolism. Disruptions in these pathways can lead to increased cancer risk, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, due to uncontrolled cell growth and bile acid imbalances.
What are the implications of this research on liver cancer treatment?
This research provides insights into the mechanisms linking bile acid metabolism with liver cancer, suggesting that targeting the YAP protein and FXR receptor may offer novel pharmacological approaches to treat or prevent hepatocellular carcinoma, thereby enhancing patient outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance | A critical imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver diseases, including liver cancer. |
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) | HCC is the most common form of liver cancer linked to bile acid imbalances. |
| Molecular Switch | Identification of a key molecular switch regulating bile provides insights for treatment options. |
| YAP’s Role | YAP inhibits FXR, leading to excess bile production, inflammation, and HCC. |
| Potential Treatments | Activating FXR or enhancing bile acid excretion could help reduce liver cancer progression. |
| Research Background | Yang’s laboratory focuses on cell signaling and its role in liver biology and tumor formation. |
Summary
Liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, is significantly influenced by bile acid imbalances in the liver. Recent studies identify a molecular switch that, when disrupted, contributes to the development of this deadly disease. Understanding these mechanisms opens new avenues for potential treatments, emphasizing the importance of bile acid regulation in liver health. By targeting the key factors involved, researchers may pave the way for new pharmacological solutions that combat liver cancer effectively.